Architecture
The DiTA platform is built as a set of Kubernetes-native microservices. It enforces a clear separation between data management (Resources), logic (Processors), and platform utilities.
Deployment Flexibility:
- Full Self-Hosting: The entire platform can be deployed on-premise for complete control.
- Hybrid: Use the public cloud for some services (e.g., the marketplace) while keeping sensitive Resource Services self-hosted.
- Service-Level: Individual services can be swapped or hosted independently.
Key Tech Stack:
- Communication: Kafka (Event Bus), gRPC/REST.
- State: PostgreSQL (Relational), Elasticsearch (Search/Index), Redis (Cache/Ephemeral).
- Identity: Keycloak.
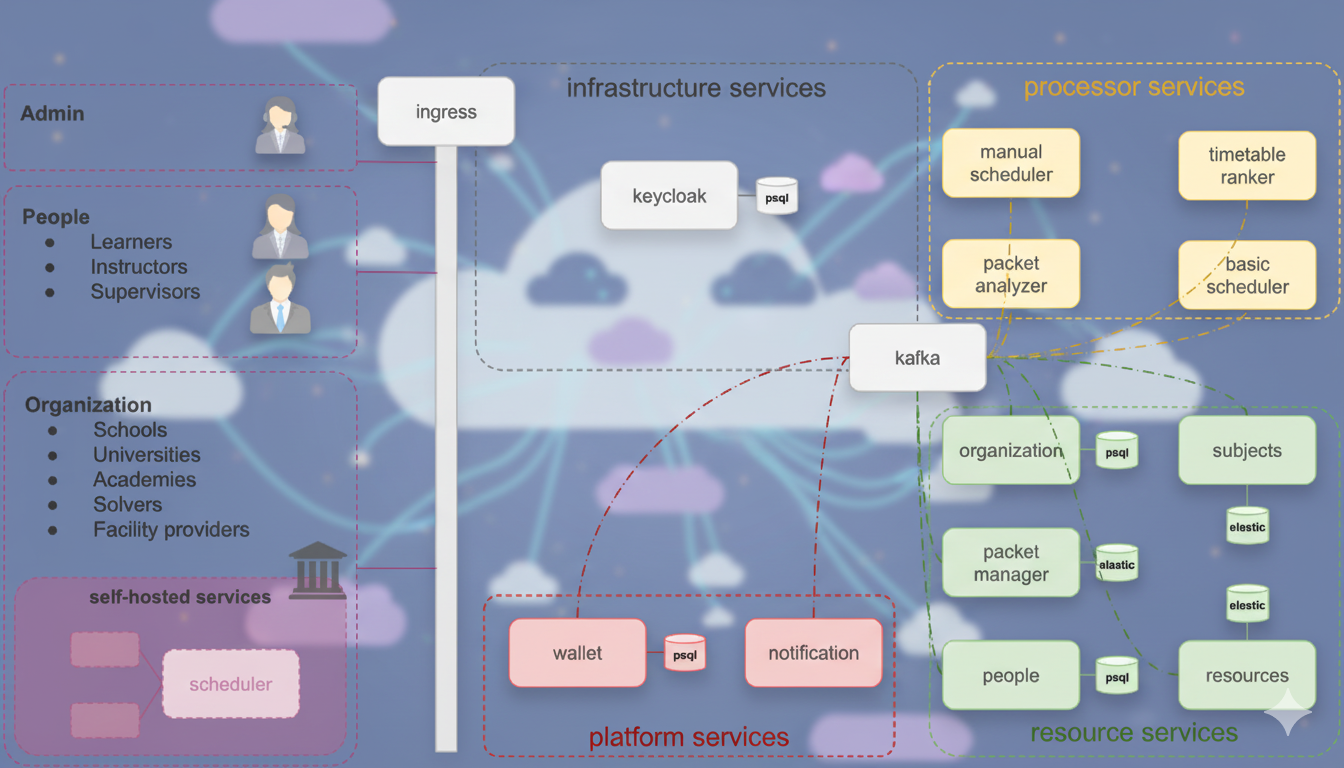
Service Groups
1. Resource Services (The "Truth")
These services manage the canonical domain data. They are the source of truth for the system.
packet-manager: Manages submission packets and their lifecycle. Uses Elasticsearch for high-performance search.people: Manages profiles (instructors, students) and availability.organization: Manages school/university metadata.resources: Manages physical assets (rooms, equipment).subjects: Manages curriculum and subject definitions.
2. Processor Services (The "Workers")
These services consume events and perform heavy lifting.
basic-scheduler: The default internal automated solver that generates timetables. Uses Redis for job queues.manual-scheduler: Supports human-in-the-loop editing.packet-analyzer: Extracts features (complexity, constraints) from packets to guide solvers.timetable-ranker: Stream processor that scores incoming solutions.
3. Platform & Infrastructure
wallet: Manages credits and transactions (Cloud-exclusive).notification: Handles alerts and messages.kafka: The central nervous system. All services publish/subscribe to domain events here.ingress: Handles routing and load balancing.
Technical Interaction Flow
The system relies on an Event-Driven Architecture:
- Ingestion: API calls to Resource Services emit events (e.g.,
packet.created) to Kafka. - Processing: Processor Services (like
basic-scheduler) subscribe to these topics. - Result Publication: Processors publish results (e.g.,
candidate.created) back to Kafka. - Aggregation: Analytics services (
timetable-ranker) consume result streams to update scores in real-time.